Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetic eye disease encompasses a group of eye conditions that can affect individuals with diabetes. Among these, diabetic retinopathy is the most common and is recognized as the leading cause of blindness among adults in the United States.
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy?
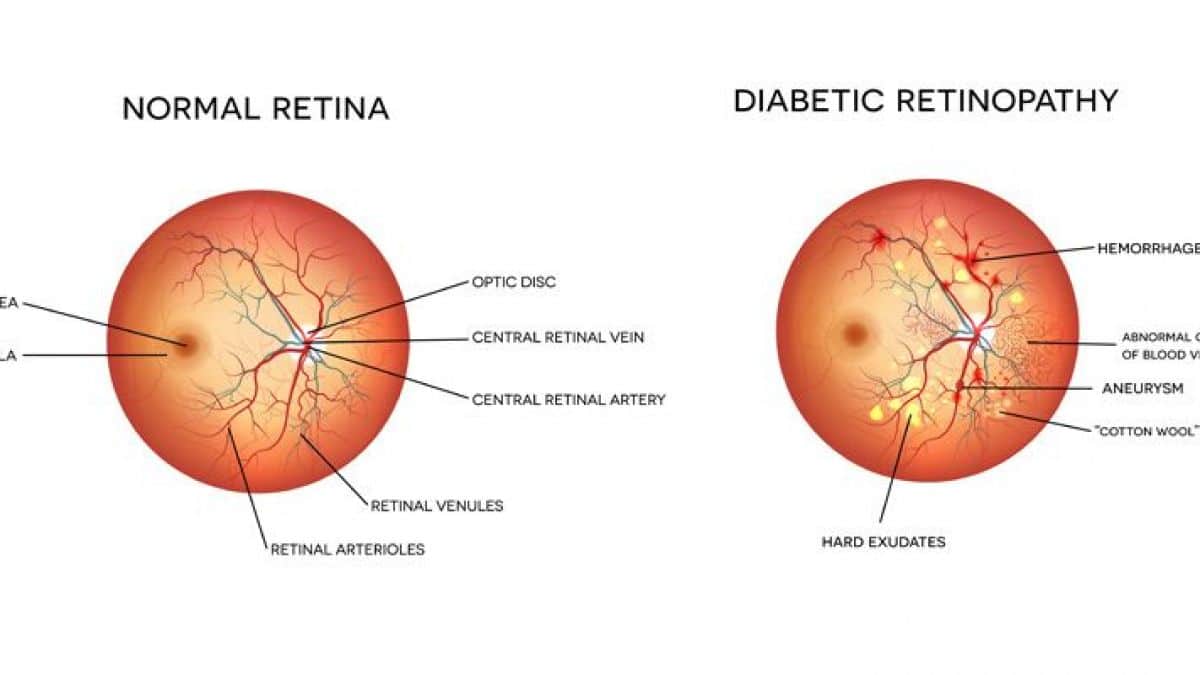
Diabetic retinopathy is a condition that affects the blood vessels of the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye responsible for visual processing. Elevated blood sugar levels can damage these blood vessels, causing them to:
- Leak blood or fluid
- Become blocked
- Form abnormal new vessels
These changes can lead to retinal damage, visual impairment, and in advanced cases, permanent vision loss.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
One of the challenges of diabetic retinopathy is that it often presents no symptoms in its early stages. Vision may remain unaffected even as the disease progresses silently. As the condition worsens, patients may experience:
- Blurred or fluctuating vision
- Dark spots or floaters
- Impaired color vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
It is important to note that diabetic retinopathy is typically painless and may go unnoticed without regular eye examinations.
Detection and Diagnosis
Diabetic retinopathy is diagnosed through a comprehensive dilated eye examination. Because early stages of the disease can be asymptomatic, annual eye exams are crucial for all individuals with diabetes-regardless of how well they are seeing. Additional specialized diagnostic tests, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) or fluorescein angiography, may be recommended to further assess retinal health.
Prevention of Diabetic Retinopathy
The best way to reduce the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy is to maintain optimal control of blood glucose levels. Additional preventive measures include:
- Managing blood pressure and cholesterol
- Avoiding tobacco use
- Attending regular eye examinations
Good systemic control can significantly decrease the likelihood of vision-threatening complications.
Treatment Options for Diabetic Retinopathy
Not all cases of diabetic retinopathy require immediate treatment. In early stages, improved diabetes management may slow or reverse the effects on the eyes. For more advanced stages, treatment options include:
Laser Therapy
Laser treatments can help seal leaking blood vessels or reduce abnormal vessel growth. These outpatient procedures are minimally invasive and generally well-tolerated.
Medications
Injections of medications-such as anti-VEGF agents-into the eye can reduce swelling, inhibit abnormal blood vessel formation, and preserve vision. These may be used alone or in combination with laser therapy.
Surgical Intervention
In severe cases, surgical procedures such as vitrectomy may be necessary to remove blood, scar tissue, or vitreous opacities. Laser treatment may be performed concurrently to improve outcomes.